In the ever-advancing realm of electronics, (Surface Mount Technology) SMT PCBA has emerged as the backbone of innovation. This article serves as a comprehensive guide, unraveling the features of SMT PCBs, explaining the inner workings of Surface Mount Technology, and delving into China’s pivotal role in providing top-notch PCBA SMT services.

The modern-day electronics world depends heavily on the Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) as its backbone. A PCB is a medium to transfer the current through its copper pathway and it dissipates the heat to keep the tiny yet highlycomplex electronic equipment on it in perfect condition.
If you are to get the best PCBA and PCB for your digital devices, you have to know this PCB assembly process thoroughly. FX PCB with its years of experience understands this need and thus, we present you the detailed guideline.
FX PCB dont follow the standerd manufacturing process is no exception to it. Our process includes solder pasting on the PCB base, placing the electronic components in the right place, soldering them with the PCB, checking the accuracy, final inspection, and delivery to customers.
Surface Mount Technology Printed Circuit Board Assembly, commonly known as SMT PCBA, stands as a groundbreaking approach to assembling electronic circuits onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike the traditional through-hole assembly, which involves inserting components through holes in the PCB, SMT PCBA strategically places components directly onto the PCB’s surface. This paradigm shift has not only revolutionized electronics manufacturing but also ushered in an era of smaller, more efficient, and higher-performance electronic devices.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) PCBs stand as the cornerstone of modern electronics manufacturing. They offer a plethora of features that have propelled them to the forefront of the industry:
Compact Design: SMT PCBs are renowned for their compactness. Components are mounted directly onto the surface of the board, eliminating the need for through-holes, resulting in sleek and space-saving designs.
High Component Density: SMT allows for a higher component density, facilitating the creation of more functional and feature-rich electronic devices.
Enhanced Performance: The shorter electrical paths in SMT designs lead to improved signal integrity, reduced interference, and ultimately, higher performance.
Cost Efficiency: Automation is a key aspect of SMT assembly, making it cost-effective for mass production. Reduced labor costs and increased production efficiency contribute to overall cost savings.
Diverse Applications: SMT PCBAs find applications in a wide range of industries, from consumer electronics to automotive and medical devices, owing to their versatility and efficiency.
Surface Mount Technology, often referred to as SMT, is a cutting-edge method of assembling electronic circuits onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional through-hole assembly, which involves inserting components through holes in the PCB, SMT places components directly onto the PCB’s surface. This technology has revolutionized electronics manufacturing.
The operation of Surface Mount Technology can be distilled into several key steps:
Component Placement: Automated machines precisely place surface-mount components onto the PCB. These components are held in position by solder paste, which acts as an adhesive.
Soldering: The PCB, now populated with components, undergoes a reflow soldering process. This process melts the solder paste, creating strong electrical connections between the components and the PCB.
Inspection: Rigorous quality control measures, including automated optical inspection, are employed to detect any defects and ensure the PCB assembly meets the highest quality standards.
Testing: Functional testing verifies that the assembled PCB operates as intended, guaranteeing it adheres to the desired specifications.
Packaging: After successfully passing quality control and functional testing, the PCBAs are packaged and prepared for distribution or integration into larger electronic devices.
Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) are the individual electronic components used in SMT PCB assembly. These components are designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB. SMDs are available in various forms, including resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), and more. They are characterized by their small size, which contributes to the compactness and efficiency of SMT PCBs.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Surface Mount Devices (SMD) are closely related but refer to different aspects of electronics manufacturing:
SMT (Surface Mount Technology): SMT is the overall assembly process that involves mounting components directly onto the PCB’s surface.
SMD (Surface Mount Device): SMDs are the individual electronic components designed for use in SMT assembly. These components have small, surface-mountable packages and are the building blocks of SMT PCBs.
The Surface Mount Technology Printed Circuit Board Assembly (SMT PCBA) process is a complex and highly efficient method of manufacturing electronic circuits. It enables the assembly of components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) with remarkable precision and reliability. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the SMT PCBA process into its key stages, giving you an in-depth understanding of how it works and why it’s vital in modern electronics manufacturing.
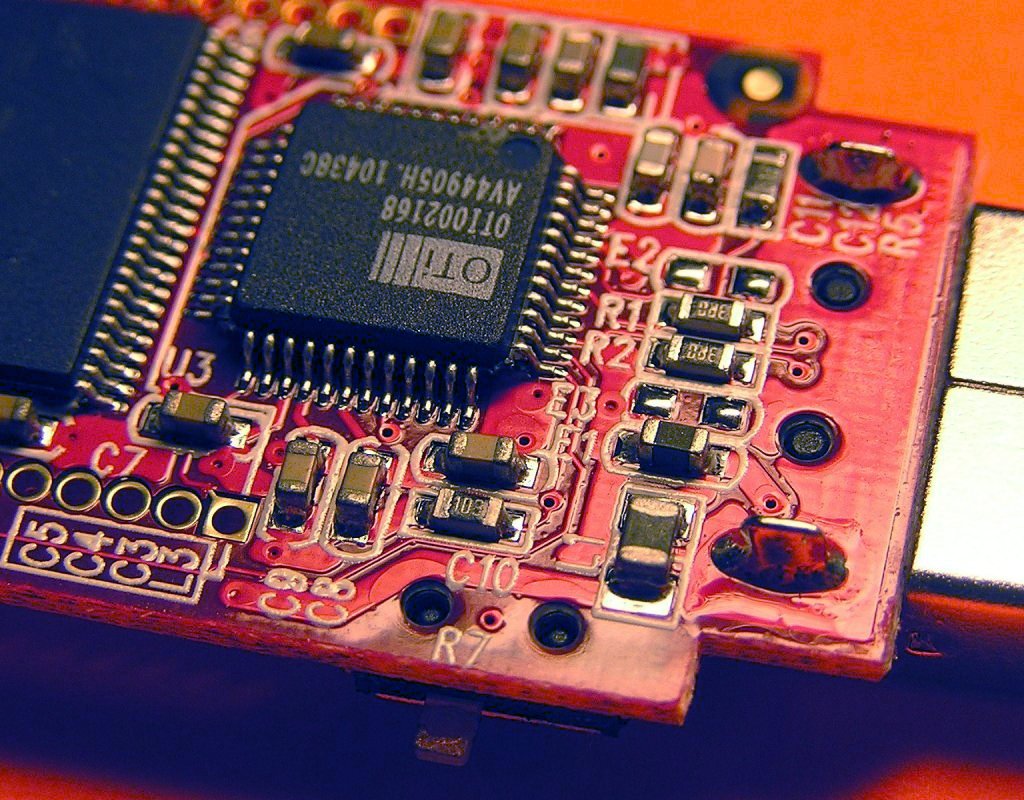
The journey of an SMT PCBA begins with meticulous design and component selection. Engineers carefully design the PCB layout, considering factors like component placement, signal routing, and board size. Component selection involves choosing the appropriate surface mount devices (SMDs), including resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), and connectors, among others. These components are essential building blocks that determine the functionality and performance of the final electronic device.
Once the design is finalized, the manufacturing process kicks off with stencil printing. A solder paste stencil, typically made of stainless steel, is used to apply solder paste to specific areas of the PCB. This stencil defines where the SMDs will be placed and soldered during the next stage. The precision and accuracy of stencil printing are crucial for ensuring that the solder paste is applied with just the right amount and in the correct locations.
Automated pick-and-place machines take center stage during component placement. These sophisticated machines are equipped with multiple nozzle heads and precise vision systems. They rapidly and accurately pick SMDs from reels, trays, or tubes and place them onto the PCB. The solder paste on the PCB serves as the adhesive, temporarily holding the components in place until they are permanently soldered in the next step. The speed and precision of these machines allow for high-volume production with consistent quality.
Reflow soldering is a critical step in the SMT PCBA process. After components are placed on the PCB, it is passed through a reflow oven. In this oven, the PCB goes through a carefully controlled temperature profile, which includes a gradual heating phase, a peak temperature phase, and a cooling phase. During the peak temperature phase, the solder paste melts and forms strong electrical connections between the SMDs and the PCB pads. The controlled temperature profile is essential to prevent overheating or damaging sensitive components.
Quality control is paramount in electronics manufacturing, and SMT PCBA is no exception. Automated optical inspection (AOI) machines and other inspection methods are employed to scrutinize the PCBAs for any defects or soldering issues. These machines use cameras and software to detect anomalies such as misaligned components, solder bridges, or missing components. Any defects found are flagged for correction before the PCBAs move to the next stage.
Functional testing is the next critical phase in the SMT PCBA process. It ensures that the assembled PCB operates as intended and meets the required specifications. Various testing methods, including in-circuit testing (ICT) and automated functional testing, are used to verify the functionality of the electronic device. This step is vital in identifying any issues that may have arisen during assembly or testing, allowing for corrections before the final product is shipped.
Once the PCBAs have successfully passed all quality checks and functional testing, they are carefully packaged and prepared for distribution or integration into larger electronic systems. Proper packaging ensures that the PCBAs remain protected during shipping and handling, minimizing the risk of damage.
China has emerged as a global powerhouse in electronics manufacturing, including the provision of PCBA SMT services. Several factors have contributed to China’s preeminence in this industry:
Cost-Effectiveness: China offers competitive labor and manufacturing costs, making it an attractive choice for outsourcing PCBA SMT services without compromising on quality.
Infrastructure and Expertise: China has made significant investments in state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and cultivated a highly skilled workforce proficient in SMT technology.
Quality Assurance: Many Chinese manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, ensuring reliable and high-quality PCBA SMT services.
Global Reach: China’s manufacturing facilities are equipped to handle large-scale production, making it a preferred choice for global companies.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) PCBs have emerged as the beating heart of modern electronics manufacturing. With features like compactness, high component density, enhanced performance, cost efficiency, and diverse applications, they continue to reshape the industry.
Understanding the essence of SMT technology, its assembly process, the role of Surface Mount Devices (SMDs), and the distinction between SMT and SMD is essential in today’s tech-driven world.
China’s leading role in providing SMT PCBA services further solidifies its position as a global leader in electronics manufacturing. Whether you’re designing cutting-edge consumer gadgets, automotive technology, or intricate medical devices, the synergy between SMT PCBs and China’s manufacturing prowess plays a vital role in shaping the future of technology.
In summation, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) PCBs are the backbone of modern electronics, and China’s expertise in offering PCBA SMT services ensures its continued leadership in innovation and production in this dynamic field.

I am Peter Gong. I have been working in PCB and PCBA industry for 15+ years now. I have been a part of the PCB revolution with my dedication to circuit board technologies and creative ideas. I write in FX PCB to impart my knowledge on PCB and PCBA for all circuit board lovers, manufacturers, and users.
WhatsApp us